Lion's mane and amanita: Medicinal properties, similarities and differences
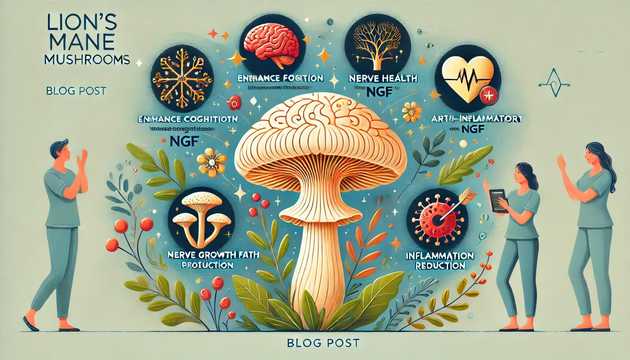
Lion's mane, whose scientific name is Hericium erinaceus, is a type of edible mushroom that has long been valued in traditional Asian medicine. Modern scientific research confirms its medicinal properties, in particular:
🔸First and foremost, Lion's mane contains unique bioactive substances, such as erinacins and hericenones, which show potential in stimulating the production of nerve growth factor (NRF). This means that the mushroom not only restores nerve connections damaged by constant stress, but also those
🔸Also, the effect of these substances is very noticeable during study, it is much easier for you to learn new material. Students like to use this effect very much.
🔸Another significant effect of Hericium erinaceus is that it "dissolves" myelin plaques thanks to the active substances erinacins.
Myelin plaques are one of the hallmarks of Alzheimer's disease.These are dense deposits of a protein known as beta-amyloid that accumulate in the brain. These plaques are thought to cause neuronal dysfunction, leading to memory loss and other cognitive impairments typical of Alzheimer's disease and dementia in general.
In addition, Hericium erinaceus in scientific studies has shown good results in the treatment of such diseases as:
🍀 Diabetes
🍀 Depression
🍀 Insomnia
🍀 Cardiovascular diseases
🍀 Ulcers and diseases of the gastrointestinal tract
🍀Inflammatory processes (Arthritis)
🍀 Low immunity
Now let's consider what the red fly agaric is capable of.
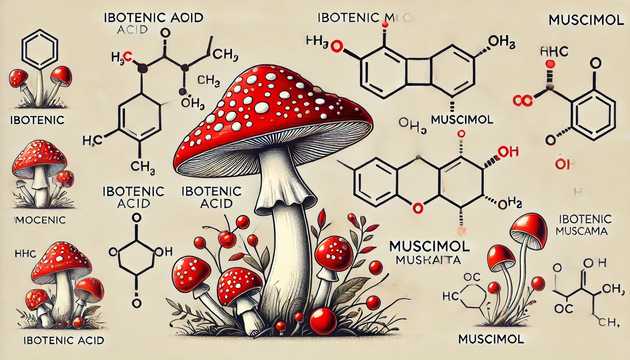
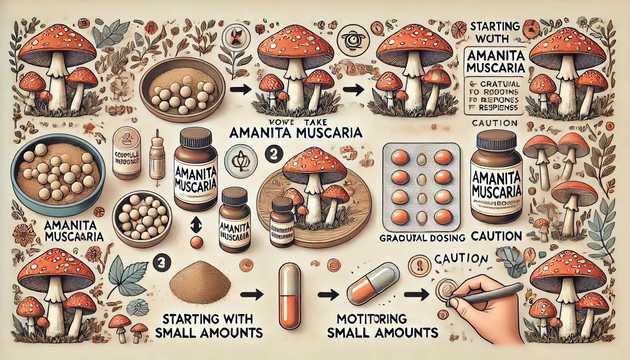
It should be noted right away that the red amanita (Amanita muscaria) is a toxic mushroom. To use this mushroom for medicinal purposes, it must be used in small doses and with caution.
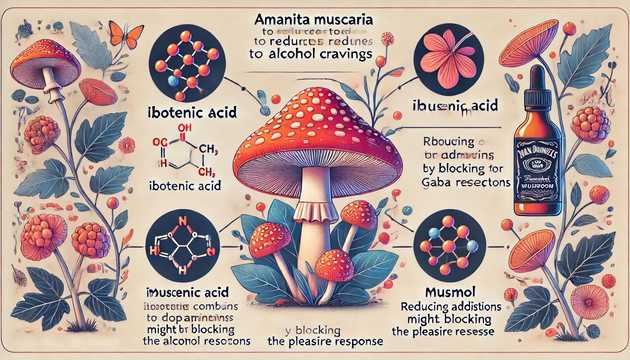
The main active components of red amanita include muscimol and ibotenic acid. These substances can affect the central nervous system, causing altered states of consciousness, hallucinations, euphoria or a sedative effect. Because of these properties, red amanita has been used in shamanic rituals in some cultures.
In numerous scientific studies, red amanita has shown itself well in the treatment of such problems as:
🔸 Depression
🔸 Insomnia
🔸 Anxiety states
🔸 Chronic fatigue
🔸 Alcoholism
🔸 Cancer
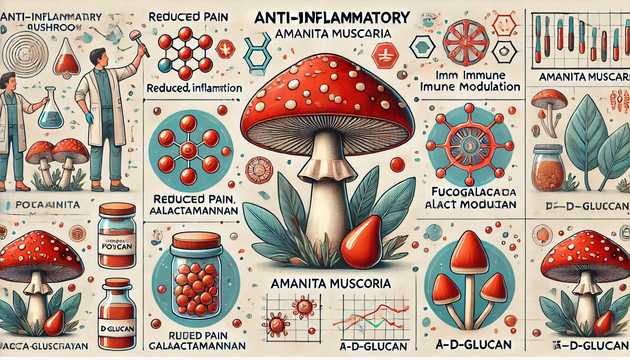
🔸Inflammatory processes
And also he:
🍀 improves memory
🍀 raises the general mood
🍀 improves clarity of thinking.
So now let's compare these two mushrooms.
The main active ingredients of these mushrooms are completely different and they affect the body in different ways. They are also very different in terms of toxicity, for example, Hericium erinaceus can be taken by children, but fly agaric can not be taken in any case.
There are problems (depression, arthritis, immunity, clarity of thought and motivation) in which it is advisable to use these two mushrooms together to enhance the therapeutic effect. However, there are cases when these two mushrooms will conflict with each other, for example, in the treatment of insomnia, especially when taken in the evening
So, in order to get the maximum benefit from taking these mushrooms separately or together (using several mushrooms at the same time has its own characteristics), we recommend that you get a consultation with us and we will help you choose the best intake scheme for you.
You can also buy them in our store.
1. Amanita fruits
2. Toadstool capsules
3. Amanita extract
4. Mushroom ground
5. lion's mane fruits
6. lion's mane capsules
7. lion's mane extract
If you found this post helpful, don’t forget to share it with your friends and colleagues.
You may also like:
![Discover the Amazing Benefits of Sea Moss for Your Health and Wellness]()
Discover the Amazing Benefits of Sea Moss for Your Health and Wellness
![The Marvel of Medicinal Mushrooms: Healing for Body and Soul]()
The Marvel of Medicinal Mushrooms: Healing for Body and Soul
![The Benefits of Lion's Mane Mushroom: A Natural Solution to Modern Lifestyle Problems]()
The Benefits of Lion's Mane Mushroom: A Natural Solution to Modern Lifestyle Problems
![The chemistry of amanita and how it affects humans]()
The chemistry of amanita and how it affects humans
![How to take a fly agaric tincture]()
How to take a fly agaric tincture
![Alcohol addiction and fly agaric]()
Alcohol addiction and fly agaric
![Lion's mane against diabetes]()
Lion's mane against diabetes
![Medicinal mushrooms against diabetes]()
Medicinal mushrooms against diabetes
![What is microdosing? Benefits, effects and how to get started]()
What is microdosing? Benefits, effects and how to get started
![How to take fly agaric: tips, dosage and benefits]()
How to take fly agaric: tips, dosage and benefits
![Is the fly agaric poisonous? Myths, facts and safety tips]()
Is the fly agaric poisonous? Myths, facts and safety tips
![How microdosing differs from antidepressants]()
How microdosing differs from antidepressants
![Suppression of inflammatory pain with the help of red fly agaric: benefits and applications]()
Suppression of inflammatory pain with the help of red fly agaric: benefits and applications
![Improving sleep with the help of red fly agaric: properties and recommendations]()
Improving sleep with the help of red fly agaric: properties and recommendations
![Lion's mane in the treatment of sciatic nerve damage: benefit and application]()
Lion's mane in the treatment of sciatic nerve damage: benefit and application
![Lion's mane is a mushroom of longevity: properties and benefits]()
Lion's mane is a mushroom of longevity: properties and benefits
![Lion's mane and Trametes versicolor: Application in supportive treatment of oncology]()
Lion's mane and Trametes versicolor: Application in supportive treatment of oncology
![Lion's mane to improve digestion: benefits and applications]()
Lion's mane to improve digestion: benefits and applications
![Clinical symptoms of red amanita poisoning: signs and help]()
Clinical symptoms of red amanita poisoning: signs and help
![What are triterpenes: properties, benefits and applications]()
What are triterpenes: properties, benefits and applications
![Lion's Mane - Improves mood and sleep in overweight or obese patients]()
Lion's Mane - Improves mood and sleep in overweight or obese patients
![Effects of Cordyceps on reproductive function in men with diabetes]()
Effects of Cordyceps on reproductive function in men with diabetes
![Cordyceps in the fight against arthritis:]()
Cordyceps in the fight against arthritis:
![Lion's Mane Against Depression: Properties and Mental Health Benefits]()
Lion's Mane Against Depression: Properties and Mental Health Benefits
![Effects of chaga extract on glucose levels, insulin secretion, and pancreatic health]()
Effects of chaga extract on glucose levels, insulin secretion, and pancreatic health
![Effect of Cordyceps militaris mushroom on vascular health: properties and benefits]()
Effect of Cordyceps militaris mushroom on vascular health: properties and benefits
![How to take the mushroom mushroom: advice and dosage]()
How to take the mushroom mushroom: advice and dosage
![Lion's mane: Useful properties and secrets of use]()
Lion's mane: Useful properties and secrets of use
![Lion's mane: Effective in fighting cardiovascular disease and cholesterol]()
Lion's mane: Effective in fighting cardiovascular disease and cholesterol
![Cordyceps: properties and health benefits]()
Cordyceps: properties and health benefits
![Discover the Amazing Benefits of Sea Moss for Your Health and Wellness]()
Discover the Amazing Benefits of Sea Moss for Your Health and Wellness
![The Marvel of Medicinal Mushrooms: Healing for Body and Soul]()
The Marvel of Medicinal Mushrooms: Healing for Body and Soul